Overview
This study aimed to measure physician accuracy for interpreting STEMI-equivalent and STEMI-mimic ECGs for catheterization laboratory activation (CLA) and compare their performance to a machine learning-based artificial intelligence algorithm, Queen of Hearts AI (QoH AI).
Published in: The American Journal of Emergency Medicine
Published on: 30 July 2025
Background
Accurate ECG interpretation is crucial to identify occlusive myocardial infarction (OMI) to determine the need for immediate catheterization laboratory activation (CLA). STEMI-equivalent and STEMI-mimic ECG patterns deviate from conventional STEMI criteria, risking misclassification of OMI cases. The diagnostic accuracy for these complex ECGs is unknown.
Methods
Fifty-three EPs and 42 cardiologists interpreted 18 ECGs (eight STEMI-equivalents, eight STEMI-mimics, with one STEMI, and a normal ECG as controls) to determine the presence of OMI requiring immediate CLA. The same ECGs were analyzed by QoH AI. Interpretations were compared against a reference standard based on angiography, troponin, echocardiography, and clinical follow-up.
Results
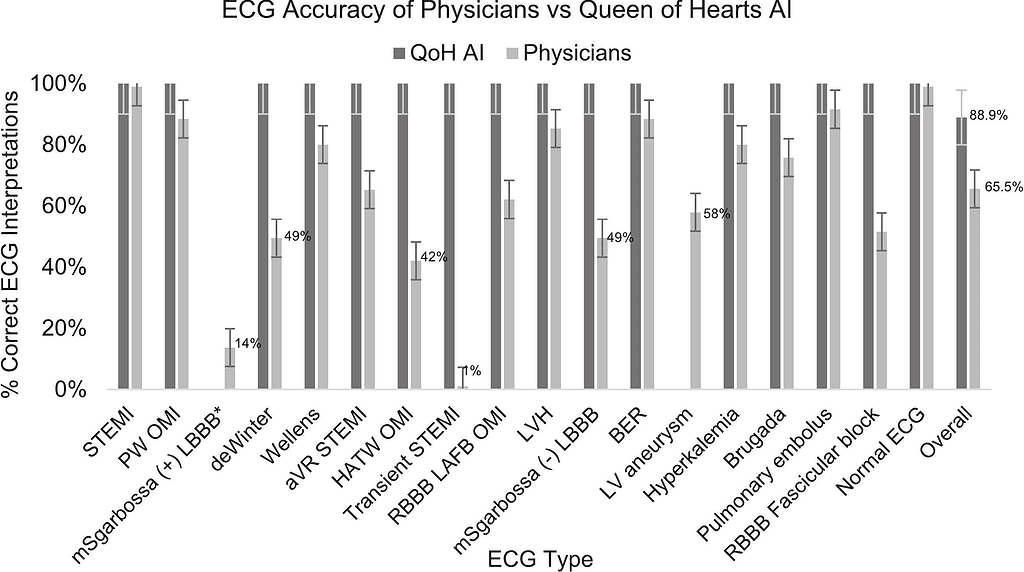
Interpretation accuracies were similar between EPs and cardiologists (65.6 %, 95 % CI [51, 78]; 65.5 %, 95 % CI [51, 77], respectively; p = 0.969), and significantly lower than QoH AI (88.9 %, 95 % CI [82, 93]) vs. physicians overall, 65.6 %, 95 % CI [52, 77]; p < 0.001). Physicians most frequently misclassified de Winter, Transient STEMI, Hyperacute T-wave OMI, and bundle branch block ECGs. QoH AI only misclassified left bundle branch block with OMI and left ventricular aneurysm without OMI.
Conclusion
Physicians frequently misinterpret STEMI-equivalent and STEMI-mimic ECGs, potentially impacting CLA decisions. QoH AI demonstrated superior accuracy, suggesting a potential to reduce missed OMIs and unnecessary catheterization laboratory activations. Prospective studies are needed to validate these findings in clinical practice.
Kyle Smiley M.D., Nathaniel Mercaldo PhD, H. Pendell Meyers M.D., Stephen W. Smith M.D.