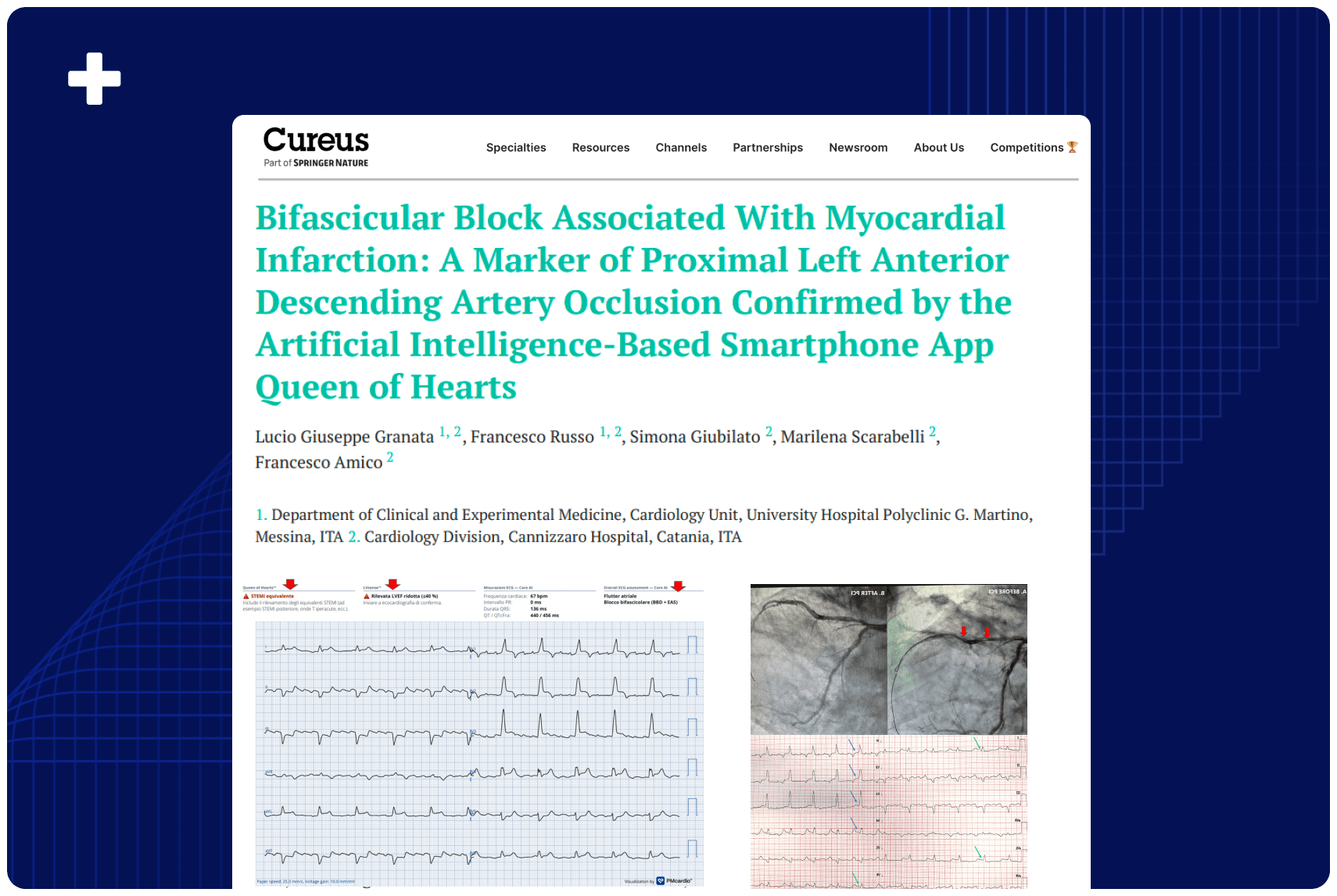
Overview:
In this single-center US-based cohort study of emergency department patients with suspected heart attacks, the PMcardio STEMI AI ECG Model outperformed standard STEMI criteria, improving detection sensitivity by 30%. Patients correctly identified by AI but missed by cardiologists faced notable treatment delays (~22 hours), underscoring the AI’s potential to enable faster diagnosis and earlier intervention.
Published In: Heart Rhythm
Presented Date: May 16, 2024
Background
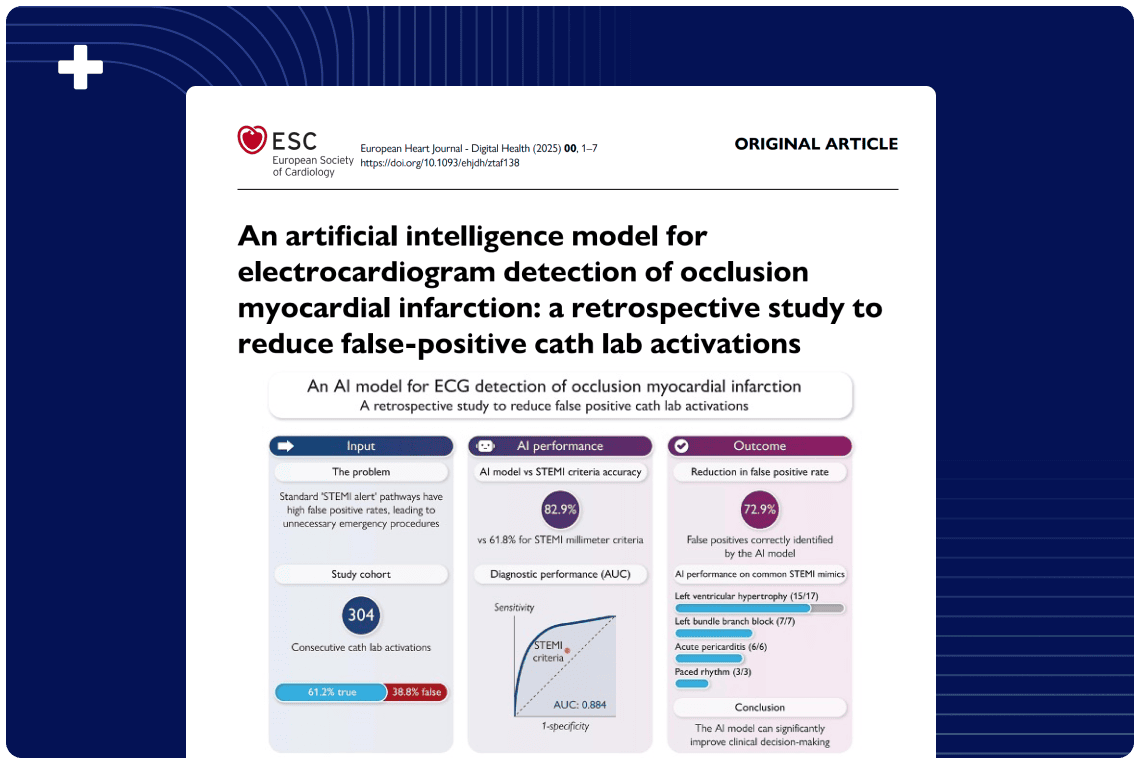
STEMI criteria have low sensitivity to detect acute coronary occlusion myocardial infarction (OMI). The Queen of Hearts (QOH) is an artificial intelligence (AI) model developed by Powerful Medical (Bratislava, Slovakia) which has been shown to outperform STEMI criteria for detection of OMI. Performance in all-comer chest pain populations is not known.
We evaluated QOH in our center in consecutive patients presenting to the emergency department (ED) with suspected acute coronary syndrome (ACS).
Methods
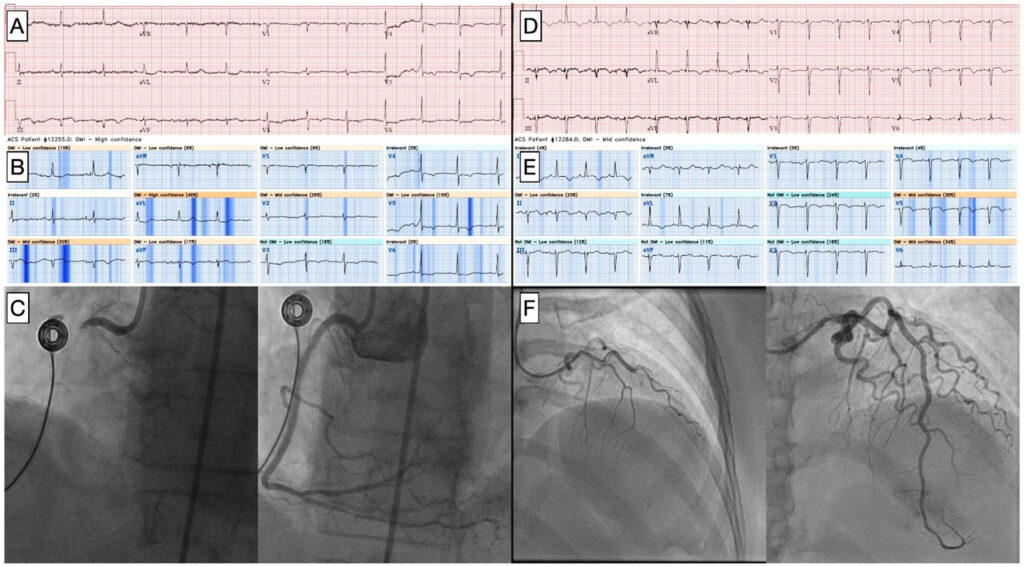
We reviewed patients who presented to our ED in October 2023 with suspected ACS. We included patients who ruled out by serial troponin or underwent angiography. Primary outcome of OMI was defined as culprit artery with TIMI flow 0-2 or culprit artery with TIMI flow 3 and high sensitivity troponin I > 5000 ng/L. Secondary outcome was door-to-device time (D2D). QOH outputs an AI interpretation (OMI or not OMI) and confidence level (low, mid, or high).
We considered OMI with mid or high confidence to be positive. For cardiologist over-read, we considered “acute MI” to be positive. We compared sensitivity using Fisher’s exact test, specificity and accuracy using Chi square, and D2D using Student’s t-test.
Results
Among 528 patients, 498 (94.3%) ruled out and 31 (17.0%) had angiography. OMI outcome was met in 10 (1.9%) and was not met in 518 (98.1%). Comparing QOH to cardiologist over-read, sensitivity was 70% vs 40%, (p=0.18), specificity was 99.2% vs 99.4% (p=NS), and accuracy was 98.7% vs 98.3% (p=0.6), respectively. For patients with QOH and cardiologist positive ECG, mean D2D was 86 ± 21 minutes. For patients with QOH positive and cardiologist negative ECG, mean D2D was 1358 ± 452 minutes (p=0.0021).
Conclusion
In our center, QOH ECG interpretation improved sensitivity for OMI by 30% without loss of specificity. QOH could expedite identification of OMI for early intervention.
Authors: William Frick, Issam Atallah, Rabya Saraf, Kuan-Yu Lin, Chien-Jung Lin, Phillip Mar