Overview
This study identifies the novel “precordial swirl sign,” a distinct ECG pattern that can uncover critical left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery blockages often missed by standard STEMI criteria. It offers a promising step toward earlier and more accurate detection of high-risk heart attacks.
Published In: Journal of Electrocardiology
Published Date: April 20, 2025
Objective
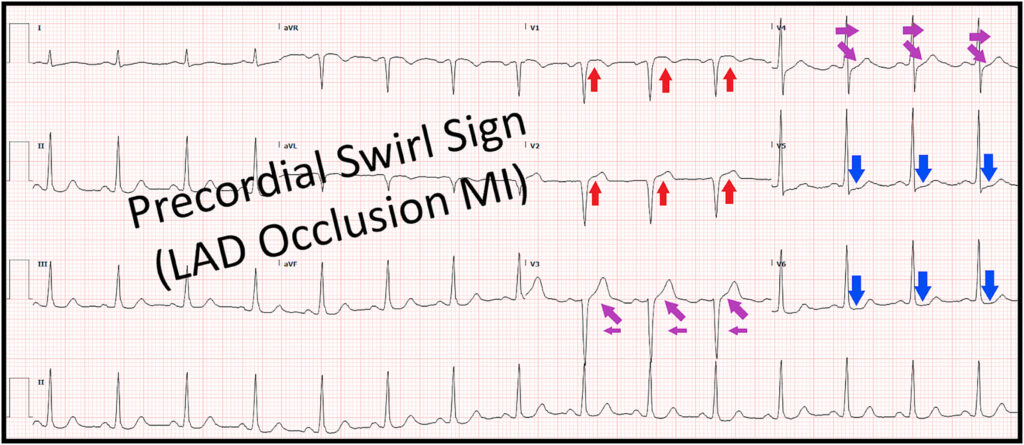
We sought to describe and evaluate an ECG pattern of left anterior descending (LAD) occlusion for which we have coined the term “precordial swirl.” In this pattern the ECG manifests abnormal ST elevation (STE) and/or hyperacute T waves in V1-V2, with reciprocal STD and/or TWI in V5-V6, creating a clockwise “swirl” pattern in the ST-T shifts of the precordial leads.
Methods
After deriving the characteristics of the precordial swirl pattern from 17 patients with proven acute LAD occlusion, the pattern was evaluated retrospectively using a high-risk population of ED patients with possible ACS symptoms. The primary outcome measures were positive predictive value and specificity for Occlusion MI for each of the developed criteria for precordial swirl sign.
Results
Several criteria were derived based on observations and measurements of the derivation cohort. The validation cohort consisted of 808 patients, of whom 265 had Occlusion MI. Precordial swirl pattern, defined as normal QRS (narrow QRS without LVH) with STD in V5 and/or V6 plus any STE in V1 and/or V2, yielded PPV 42 %, sensitivity 11 %, (95 % CI 8–15 %), and specificity 92 % (95 % CI 90–95 %) for Occlusion MI. When defined as a narrow QRS plus STD in V5/V6 plus T wave to S wave amplitude ratio > 0.40 in V2, precordial swirl pattern yielded PPV 70 %, sensitivity 9 %, specificity 98 %. Of the 23 Occlusion MI patients correctly identified by precordial swirl sign, 19 (83 %) had LAD culprit lesions, and 16 (70 %) were missed by STEMI criteria.
Conclusion
Among high-risk ACS patients in the ED, precordial swirl sign had clinically relevant PPV and specificity for LAD Occlusion MI, including a significant number of patients who are missed by the current STEMI criteria. Further study should be done to validate these findings and improve detection of acute coronary occlusion myocardial infarction.
Authors: Lucas Goss, H. Pendell Meyers, Brandon Friedman, Stephen W. Smith