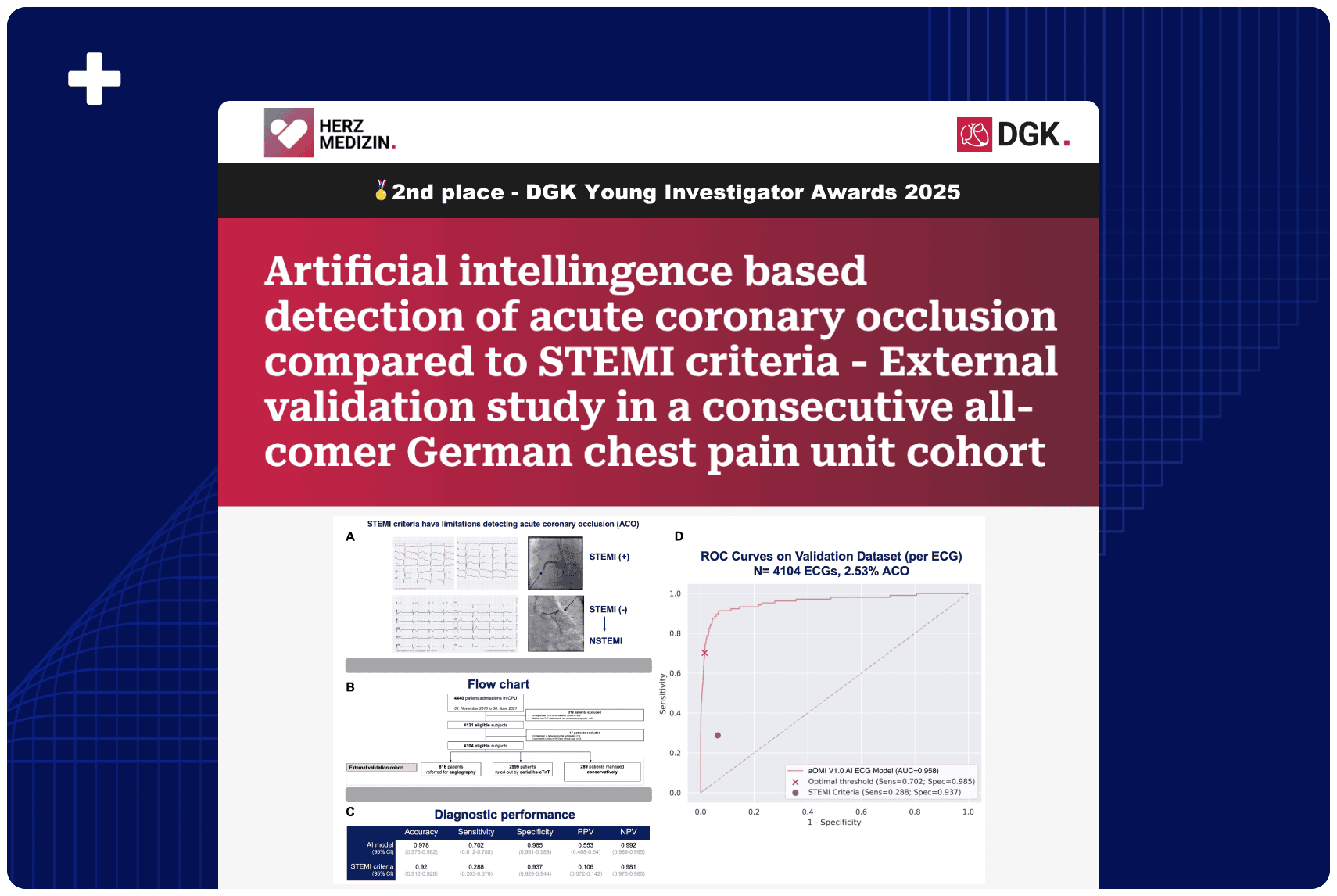
Overview:
Traditional ECG criteria miss nearly one-third of heart attack patients with a fully occluded artery, mislabeling them as “NSTEMI” despite needing urgent care. This retrospective study of 10,000 patients found they face longer treatment delays and nearly double the one-year mortality of “acute” STEMI patients, highlighting the need for better ECG-based risk stratification and faster intervention.
Published In: European Heart Journal
Presented Date: November 9, 2023
Background
The prognosis of STEMI and NSTEMI patients stratified according to invasive angiographic findings of an occluded culprit coronary, i.e., occlusion myocardial infarction (OMI), remains unclear.
This retrospective single-center study aimed to compare the clinical presentation, management, and all-cause mortality of STEMI, NSTEMI-OMI, and NSTEMI-Non-OMI (NSTEMI-NOMI).
Methods
Demographics, clinical and procedural data were pooled for all patients with an index ACS event between January 2011 and May 2021. Patients were classified according to the presence of OMI determined by angiography and troponin. All-cause mortality was compared by Kaplan Meier analysis at 1-year and landmark analysis up to 5 years after the ACS event.
Results
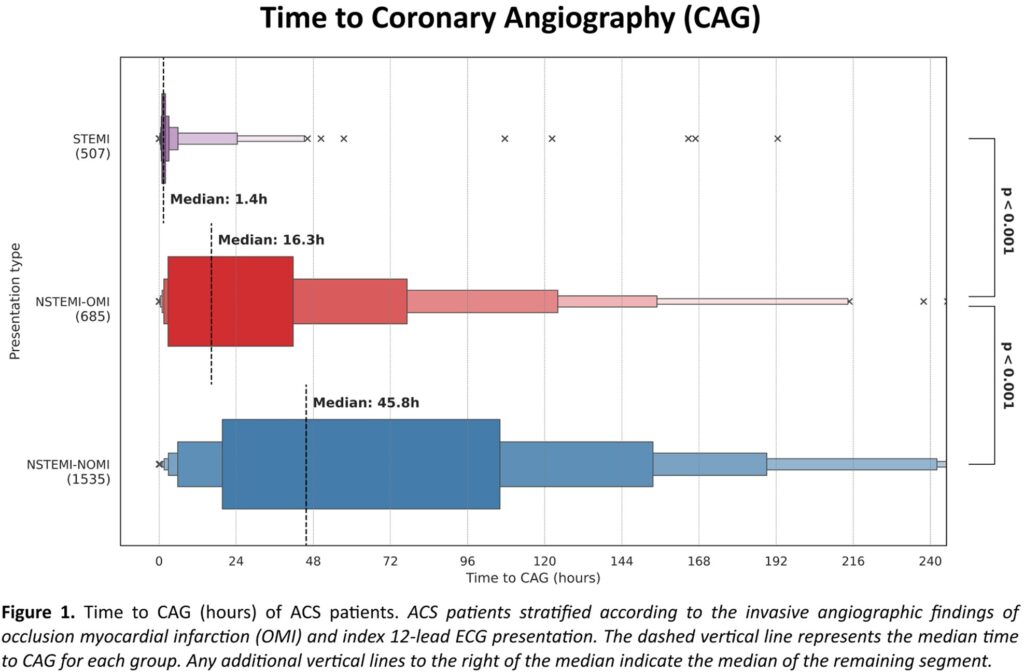
A total of 9,943 patients [64.1 ± 14.2 years, 62.2% males] were included and classified into STEMI (n=507), NSTEMI-OMI (n=685), NSTEMI-NOMI (n=1,535) and MI ruled-out (n=7,216). Median time to coronary angiography (CAG) was 1.4 hours for STEMI compared to 16.3 and 45.8 hours for NSTEMI-OMI and NSTEMI-NOMI, respectively (p<0.001) [Figure 1].
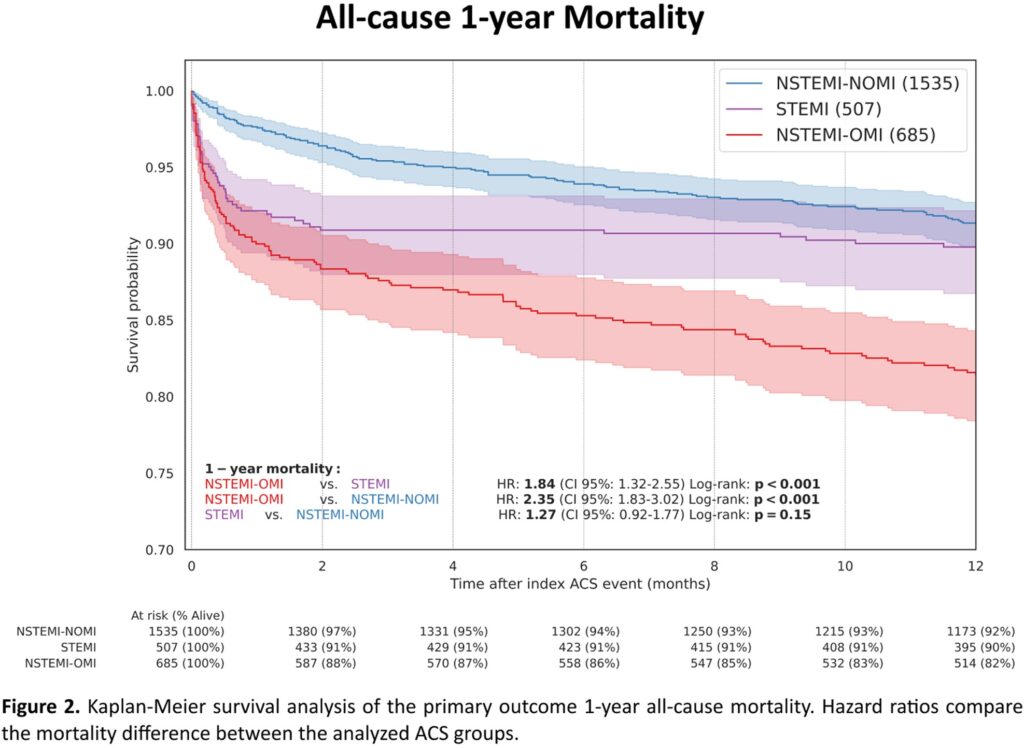
At one year, all-cause mortality occurred in 9.9% of STEMI patients vs. 18.1% of NSTEMI-OMI patients (hazard ratio, 1.84; 95% CI, 1.32 to 2.55; p<0.001) and 7.9% of NSTEMI-NOMI patients (hazard ratio, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.56 to 1.09; p=0.150) [Figure 2]. An unfavorable mortality outcome for NSTEMI-OMI compared to STEMI was maintained in the age and gender-adjusted analyses and landmark analysis beyond 1-year (hazard ratio, 2.59; 95% CI, 1.75 to 3.82; p<0.001).
Conclusion
Despite similar baseline demographics and angiographic findings, patients with NSTEMI-OMI have increased delays to reperfusion and unfavorable short and long-term all-cause mortality compared to STEMI. These findings support the need for more accurate and timely identification of NSTEMI-OMI.
Authors: R Herman, S W Smith, H P Meyers, D T Bertolone, A Leone, K Bermpeis, M Viscusi, M Martonak, J Bahyl, A Demolder, L Perl, W Wojakowski, J Bartunek, E Barbato