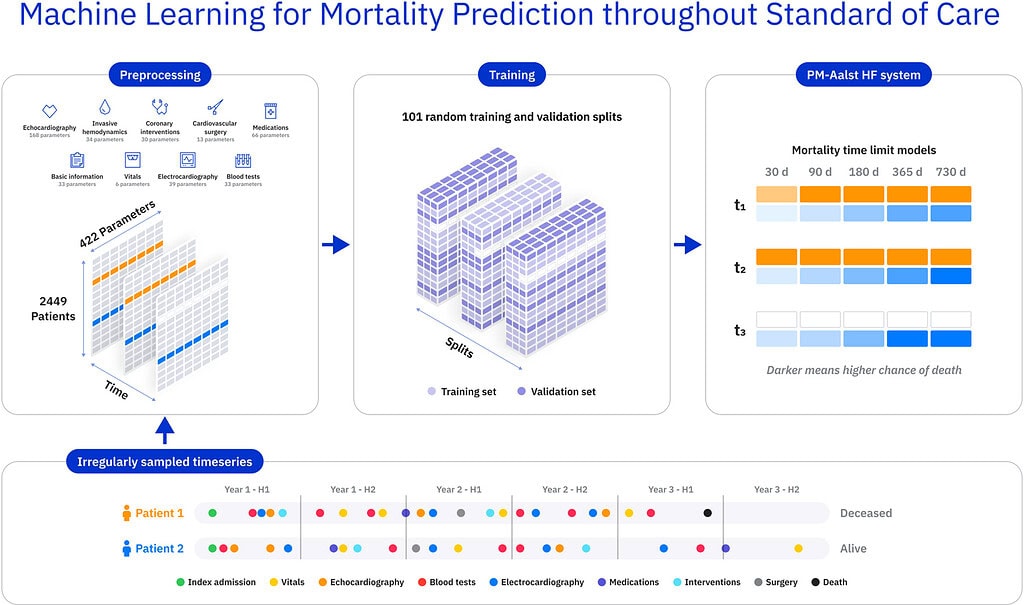
Overview:
In collaboration with the Cardiovascular Center Aalst in Belgium, Powerful Medical developed a machine learning algorithm to improve risk stratification in patients hospitalized with new or worsening heart failure. Trained on 2,449 patients and 151,451 exams, the model accurately predicts mortality across multiple time points (AUC-ROC 0.83–0.89), enabling proactive, yet personalized clinical interventions.
Published In: ESC Heart Failure
Published on: June 13, 2022
Aims
Risk stratification in patients with a new onset or worsened heart failure (HF) is essential for clinical decision making. We have utilized a novel approach to enrich patient level prognostication using longitudinally gathered data to develop ML-based algorithms predicting all-cause 30, 90, 180, 360, and 720 day mortality.
Methods
In a cohort of 2,449 HF patients hospitalized between 1 January 2011 and 31 December 2017, we utilized 422 parameters derived from 151,451 patient exams. They included clinical phenotyping, ECG, laboratory, echocardiography, catheterization data or percutaneous and surgical interventions reflecting the standard of care as captured in individual electronic records. The development of predictive models consisted of 101 iterations of repeated random subsampling splits into balanced training and validation sets.
Results
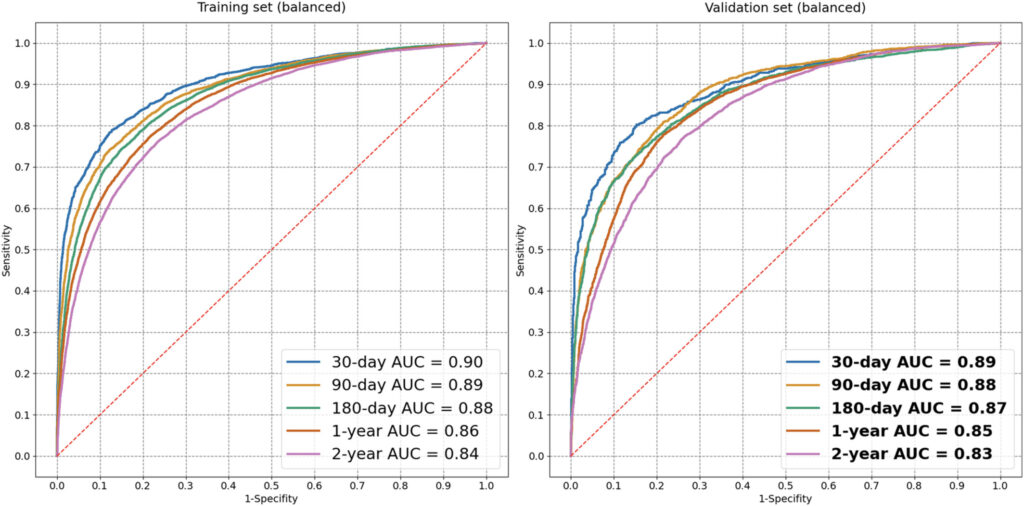
ML models yielded area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC-ROC) performance ranging from 0.83 to 0.89 on the outcome-balanced validation set in predicting all-cause mortality at aforementioned time-limits. The 1 year mortality prediction model recorded an AUC of 0.85. We observed stable model performance across all HF phenotypes: HFpEF 0.83 AUC, HFmrEF 0.85 AUC, and HFrEF 0.86 AUC, respectively. Model performance improved when utilizing data from more hospital contacts compared with only data collected at baseline.
Conclusion
Our findings present a novel, patient-level, comprehensive ML-based algorithm for predicting all-cause mortality in new or worsened heart failure. Its robust performance across phenotypes throughout the longitudinal patient follow-up suggests its potential in point-of-care clinical risk stratification.
Authors: Robert Herman, Marc Vanderheyden, Boris Vavrik, Monika Beles, Timotej Palus, Olivier Nelis, Marc Goethals, Sofie Verstreken, Riet Dierckx, Martin Penicka, Ward Heggermont, Jozef Bartunek