Overview:
As the leading publication in EHJ-Digital Health for the past year, this study presents the internal multi-centric validation of the PMcardio STEMI AI ECG Model for detecting acute coronary blockage. Trained on 18,616 ECGs, the model achieved an AUC of 0.938, with 80.6% sensitivity and 93.7% specificity. It significantly outperformed traditional STEMI criteria and matched expert interpretation, offering a groundbreaking advancement in emergent patient detection.
Published In: European Heart Journal – Digital Health
Published on: November 28, 2023
Aims
A majority of acute coronary syndromes (ACS) present without typical ST elevation. One-third of non–ST-elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) patients have an acutely occluded culprit coronary artery [occlusion myocardial infarction (OMI)], leading to poor outcomes due to delayed identification and invasive management.
In this study, we sought to develop a versatile artificial intelligence (AI) model detecting acute OMI on single-standard 12-lead electrocardiograms (ECGs) and compare its performance with existing state-of-the-art diagnostic criteria.
Methods
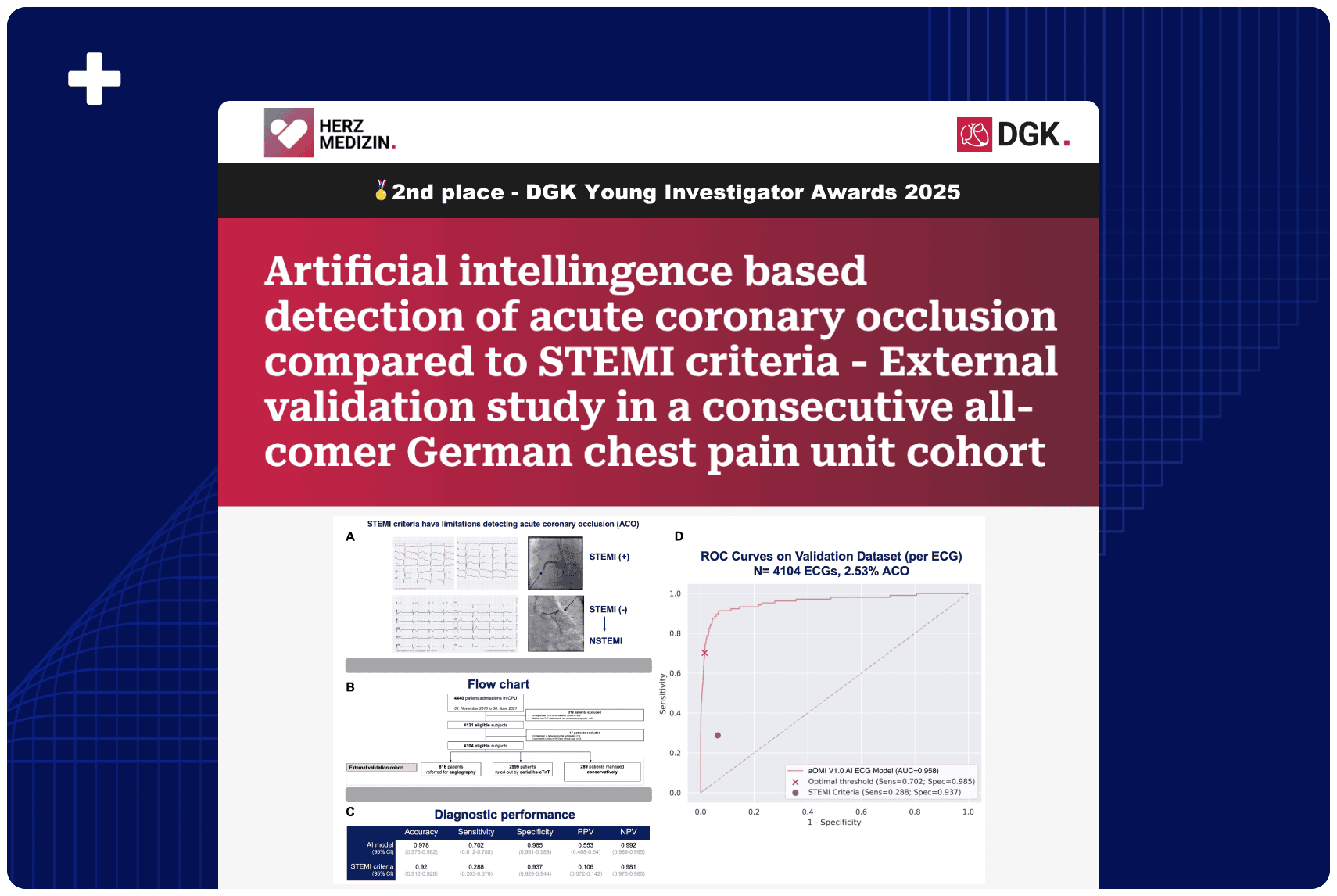
An AI model was developed using 18,616 ECGs from 10,543 patients with suspected ACS from an international database with clinically validated outcomes. The model was evaluated in an international cohort and compared with STEMI criteria and ECG experts in detecting OMI. The primary outcome of OMI was an acutely occluded or flow-limiting culprit artery requiring emergent revascularization.
Results
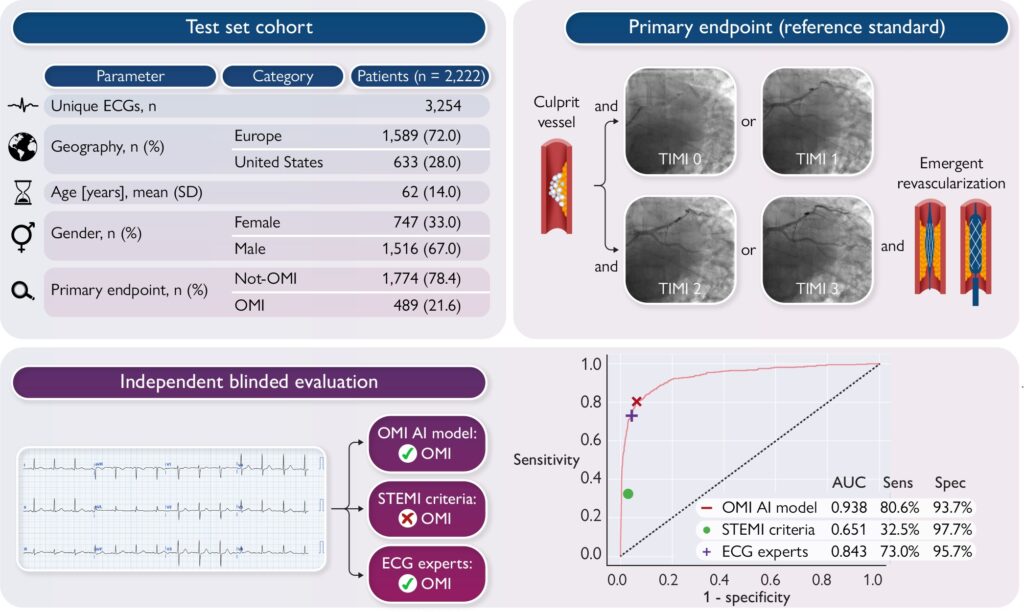
In the overall test set of 3,254 ECGs from 2,222 patients (age 62 ± 14 years, 67% males, 21.6% OMI), the AI model achieved an area under the curve of 0.938 [95% confidence interval (CI): 0.924–0.951] in identifying the primary OMI outcome, with superior performance [accuracy 90.9% (95% CI: 89.7–92.0), sensitivity 80.6% (95% CI: 76.8–84.0), and specificity 93.7 (95% CI: 92.6–94.8)] compared with STEMI criteria [accuracy 83.6% (95% CI: 82.1–85.1), sensitivity 32.5% (95% CI: 28.4–36.6), and specificity 97.7% (95% CI: 97.0–98.3)] and with similar performance compared with ECG experts [accuracy 90.8% (95% CI: 89.5–91.9), sensitivity 73.0% (95% CI: 68.7–77.0), and specificity 95.7% (95% CI: 94.7–96.6)].
Conclusion
The present novel ECG AI model demonstrates superior accuracy to detect acute OMI when compared with STEMI criteria. This suggests its potential to improve ACS triage, ensuring appropriate and timely referral for immediate revascularization.
“This study has several implications for the future management of ACS. The OMI AI model paired with digitization technology offers an accurate detection of patients with OMI using single-standard 12-lead ECG.
Such accurate and timely ECG-based ACS diagnosis at the time of first patient contact could prompt a swift coronary intervention as recommended currently in the case of standard STEMI criteria.“
Authors: Robert Herman, Harvey Pendell Meyers, Stephen W Smith, Dario T Bertolone, Attilio Leone, Konstantinos Bermpeis, Michele M Viscusi, Marta Belmonte, Anthony Demolder, Vladimir Boza, Boris Vavrik, Viera Kresnakova, Andrej Iring, Michal Martonak, Jakub Bahyl, Timea Kisova, Dan Schelfaut, Marc Vanderheyden, Leor Perl, Emre K Aslanger, Robert Hatala, Wojtek Wojakowski, Jozef Bartunek, Emanuele Barbato