Overview
Up to a third of high-risk heart attacks go unrecognized by traditional ECG diagnostic criteria, causing dangerous delays—an effect even more pronounced in women, who remain understudied in this context. This analysis reveals a 4.4-hour treatment delay for initially misclassified female patients compared to males, highlighting the urgent need for modern, unbiased diagnostic solutions.
Published In: Circulation (AHA Journals) – presented at the American Heart Association (AHA) 2024 Scientific Sessions
Presented Date: November 11, 2024
Background
Sex disparities in symptom presentation are well-documented in female patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS). Moreover, nearly half of the patients with acutely occlusive myocardial infarction (OMI) do not meet the STEMI criteria at admission, leading to delays in receiving emergent reperfusion. This delay may be more pronounced in female OMI patients without ST-elevation (NSTEMI-OMI), potentially due to differences in symptom presentation and recognition.
Purpose
To investigate disparities in delays from admission ECG to percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) between male and female patients with acute OMI stratified according to the presence of STEMI criteria.
Methods
Electrocardiograms (ECGs), laboratory and coronary angiography (CAG) data were sourced from a total of 623 consecutive OMI patients from five international cohorts from 2012 to 2023. The final diagnosis of OMI was adjudicated by two expert physicians based on all available data. Patients were stratified into STEMI-OMI and NSTEMI-OMI based on their initial admission ECG and time-to-PCI: <2hrs vs. >2hrs, respectively. Each cohort was further subdivided based on sex (male vs. female).
Results
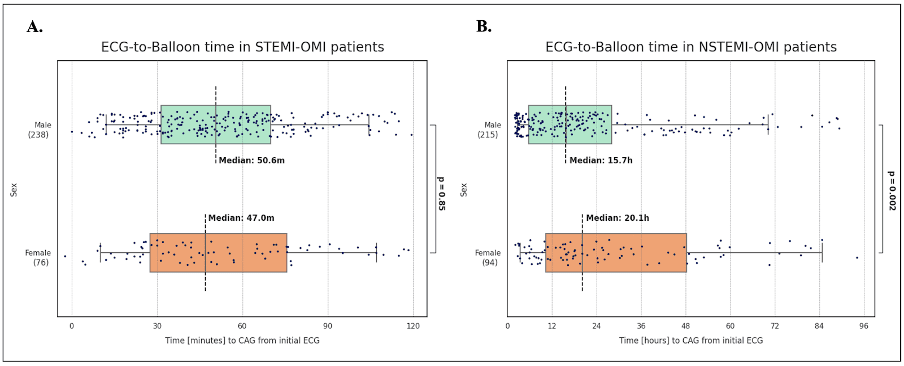
A total of 314 STEMI-OMI patients (24% female) and 309 NSTEMI-OMI (30% female) were included in the analysis. Median ECG-to-balloon (E2B) time between STEMI-OMI and NSTEMI-OMI patients was 48 minutes and 17.1 hours, respectively (p<0.001). Female STEMI-OMI patients had an E2B of 47.0 minutes (95% CI: 30-78), compared to 50.6 minutes (95% CI: 30-72) for male patients, respectively, and did not differ significantly (p=0.85) (Fig 1A). In NSTEMI-OMI, female patients had a significantly longer median E2B time of 20.1 hours (95% CI: 10.2-48.2) as compared to 15.7 hours (95% CI: 5.6-28.0) (p=0.002) in male patients (Fig 1B).
Conclusion
The present international multi-centric validation of consecutive patients with acute coronary occlusion reveals a significant sex disparity in NSTEMI-OMI patients, with female patients experiencing a 4.4-hour delay to reperfusion compared to males. These findings highlight the need for unbiased diagnostic strategies to address sex differences in ACS presentation.
Authors: Timea Kisova, MD, BSc, Robert Herman, MD, Anthony Demolder, MD, MSc, PhD, Jakub Bahyl, Mgr, Hana Hybasek Dzurikova, MRCVS, PGCert MEd, Stephen Smith, MD, Harvey Meyers, MD, Mark Hellerman, MD, Rinaldo Lauwers, MD, David Pletnickx, MD, Dan Schelfaut, MD, Fadi El Ters, MD, Alain Tanios, MD, Fabrizio Ricci, MD, PhD, MSc, Davide Rossi, MD, Jozef Bartunek, Prof.,MUDr.,PhD, and Emanuele Barbato, Prof.,MD