Overview:
This comprehensive review highlights the limitations of the traditional STEMI/NSTEMI classification for heart attacks and advocates for a more precise approach to diagnosis and patient triage. Instead of relying solely on standard ECG criteria, this method focuses on ECG patterns that more accurately reflect the severity of underlying coronary vessel disease.
By identifying high-risk ECG changes beyond current STEMI guidelines, clinicians can detect heart attacks earlier, initiate treatment faster, and ultimately improve patient outcomes.
Introduction:
The traditional management of acute coronary syndrome has relied on the identification of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) as a proxy of acute coronary occlusion. This conflation of STEMI with acute coronary occlusion has historically overshadowed non–ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI), despite evidence suggesting 25% to 34% of NSTEMI cases may also include acute coronary occlusion.
Current limitations in the STEMI/NSTEMI binary framework underscore the need for a revised approach to chest pain and acute coronary syndrome management.
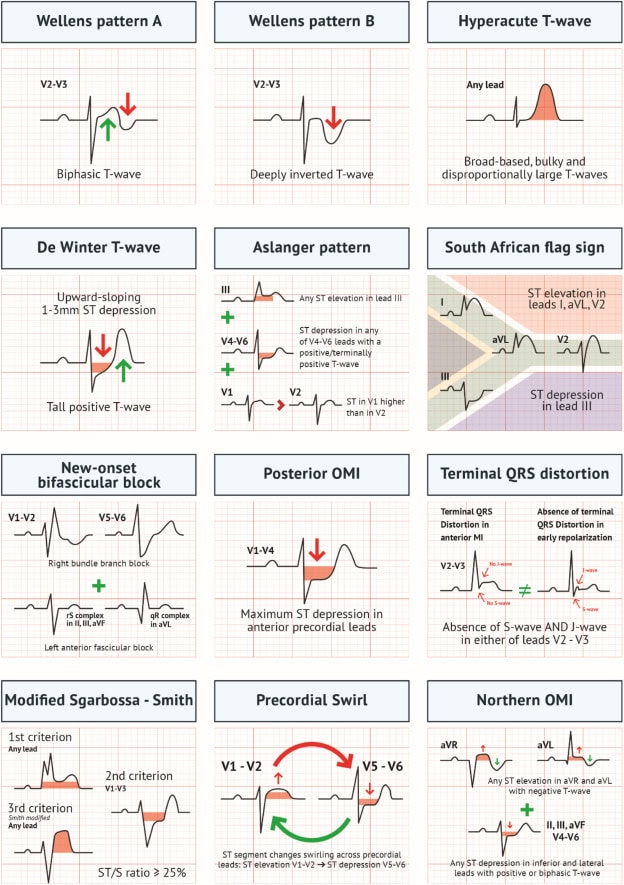
The emerging paradigm distinguishing occlusion myocardial infarction from nonocclusion myocardial infarction (NOMI) seeks to enhance diagnostic accuracy and prognostic effect in acute coronary syndrome care.
This approach not only emphasizes the urgency of reperfusion therapy for high-risk ECG patterns not covered by current STEMI criteria, but also emphasizes the broader transition from viewing acute coronary syndrome as a disease defined by the ECG to a disease defined by its underlying pathology, for which the ECG is an important but insufficient surrogate test.
This report outlines the emerging occlusion myocardial infarction paradigm, detailing specific ECG patterns linked to acute coronary occlusion, and proposes a new framework that could enhance triage accuracy and treatment strategies for acute coronary syndrome.
Although further validation is required, the occlusion myocardial infarction pathway holds promise for earlier acute coronary occlusion detection, timely cath lab activation, and improved myocardial salvage—offering potentially significant implications for both clinical practice and future research in acute coronary syndrome management.
Authors List:
Fabrizio Ricci, MD, PhD; Chiara Martini, MD; Davide Maria Scordo, MD; Davide Rossi, MD; Sabina Gallina, MD; Artur Fedorowski, MD, PhD; Luigi Sciarra, MD; C. Anwar A. Chahal, MD, PhD; H. Pendell Meyers, MD; Robert Herman, MD; Stephen W. Smith, MD