Overview
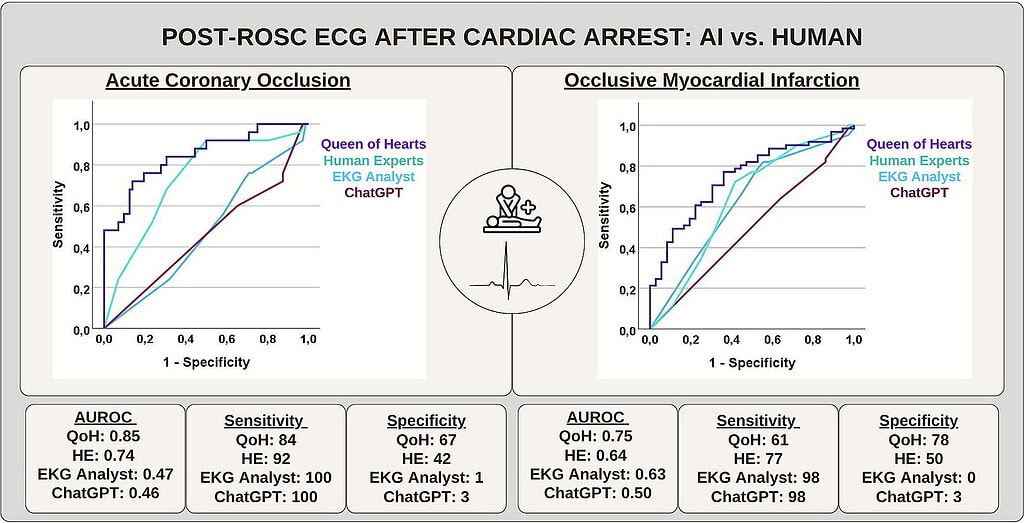
This single-centre study tested whether AI-based ECG analysis can detect occlusive myocardial infarction (OMI) after cardiac arrest using post-ROSC ECGs from 97 patients with subsequent coronary angiography. A dedicated deep neural network (Queen of Hearts, QoH) achieved the highest discrimination for acute coronary occlusion (AUC 0.85) and OMI (AUC 0.75), outperforming human experts, with a more balanced trade-off between sensitivity and specificity. In contrast, two large language model–based chatbots (ChatGPT and a GPT-based EKG Analyst) showed near-perfect sensitivity but almost no specificity, labelling nearly all ECGs as OMI and thus providing no meaningful diagnostic discrimination. These findings suggest that specialized ECG-trained AI, such as QoH, may serve as a useful adjunct in post-resuscitation decision-making. In contrast, general-purpose LLMs are currently unsuitable for critical ECG diagnosis.
Published in: Resuscitation
Published on: 19 November 2025
Background
Accurate electrocardiogram (ECG) interpretation after cardiac arrest is essential for identifying occlusive myocardial infarction (OMI), but post-resuscitation artifacts make this challenging. While artificial intelligence (AI) offers promising support, its diagnostic performance in this critical setting remains uncertain.
Methods
This single-centre study included 97 adult patients resuscitated from cardiac arrest (CA). Post-return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC), ECGs were evaluated by four methods: human experts (HE), a validated deep neural network (Queen of Hearts [QoH]), and two large language model (LLM)–based AI chatbots (AI-CB) – ChatGPT and EKG Analyst. The primary outcome was the AUROC for the presence and probability of OMI and acute coronary occlusion (ACO), determined by coronary angiography.
Results
For ACO (TIMI 0), QoH yielded the highest AUROC (0.846 [0.752–0.939]), followed by HE (0.735 [0.622 – 0.848]). Both AI-CB resulted in the lowest AUROC (ChatGPT: 0.456 [0.319 – 0.592]; EKG Analyst: 0.474 [0.346 – 0.603]. For OMI (TIMI 0-2 or TIMI 3 + peak-troponin), QoH again achieved the highest AUROC (0.745 [0.647 – 0.843]), followed by HE (0.635 [0.515 – 0.755]), AI-CB were lowest again (ChatGPT: 0.495 [0.376 – 0.614]; EKG Analyst: 0.626 [0.508 – 0.743]. Threshold-dependent performance metrics revealed high sensitivity (ACO: 100%; OMI: 98.36%) for both AI-CB, at the cost of minimal specificity. QoH and HE showed more even distributions of sensitivity/specificity.
Conclusion
QoH, despite operating without awareness of the CA-setting and thus likely at a relative disadvantage, and HE showed robust diagnostic accuracy. Due to undifferentiated overdiagnosis, general LLMs remain unsuitable for ECG interpretation. Domain-specific tools, such as QoH, may offer complementary value.