Overview
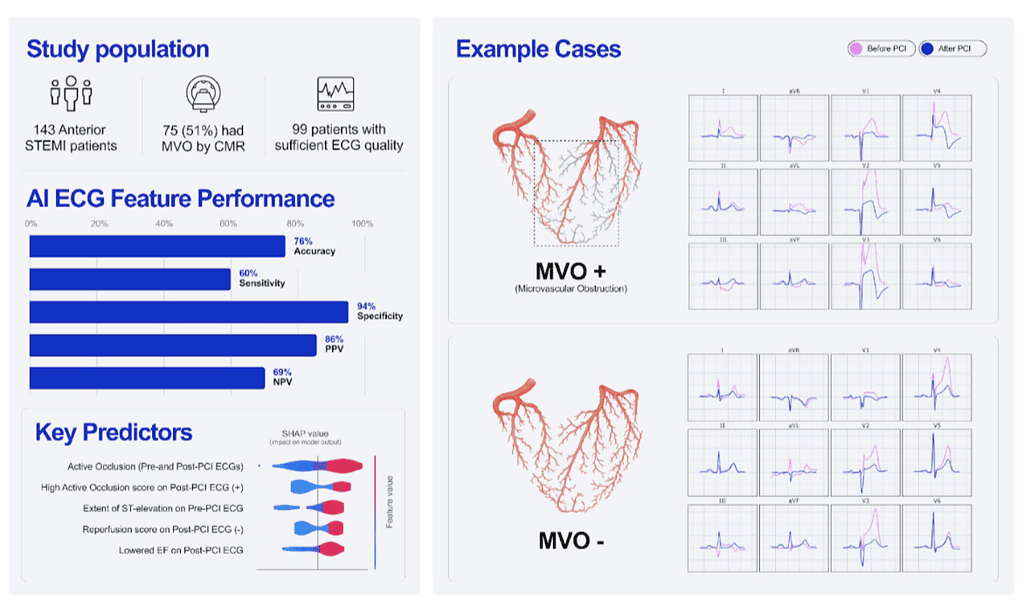
This study tested whether artificial intelligence (AI)–extracted electrocardiogram (ECG) features can identify microvascular obstruction (MVO) after reperfusion in anterior ST‑segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). Using pre‑ and post‑percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) ECGs and a logistic‑regression model built on PMcardio (API v2.5), the AI approach predicted CMR‑confirmed MVO with an AUC of 0.83, 94% specificity, and 60% sensitivity; the figure reports ~76% overall accuracy. By emphasizing high specificity, the model aims to flag patients very likely to harbor MVO when cardiac MRI is impractical, enabling rapid risk stratification at the point of care.
Published in: Circulation: Cardiovascular Interventions
Published on: 10 November 2025
Background
MVO after primary PCI is a powerful marker of poor prognosis—linked to adverse left‑ventricular remodeling, increased major adverse cardiac events, and higher mortality—yet the gold‑standard test (gadolinium CMR) is costly, time‑consuming, and not universally available. Persistent ST‑segment elevation on post‑PCI ECGs is common with MVO, suggesting ECG‑based signatures might serve as a noninvasive surrogate. The investigators therefore evaluated whether AI‑derived ECG features could reliably indicate the presence of MVO without relying on CMR.
Methods
In a single‑center retrospective cohort of anterior STEMI patients (143 total; 99 with analyzable paired pre‑ and post‑PCI ECGs), all underwent pre‑discharge CMR for MVO and infarct size measurement. Anonymized ECGs were processed by the PMcardio AI system to extract features previously associated with acute coronary occlusion, reperfusion, and cardiac dysfunction; cases with unusable AI output comprised 10 patients (6.9% of the total). A logistic‑regression model was trained and evaluated with five‑fold cross‑validation; performance was summarized by sensitivity, specificity, positive/negative predictive values, and AUC, and feature importance was assessed using SHAP values. Institutional review board approval and informed consent were obtained.
Results
Patients with MVO (n=74) and without MVO (n=69) were similar in age, but fewer females had MVO (6 vs 19; p<0.01); median MVO mass was 16 g (IQR 9–32), and infarct size was larger with MVO (59 g [46–82] vs 24 g [14–38]; p<0.001). The AI ECG model achieved an AUC of 0.83 with 94% specificity, 60% sensitivity, PPV 86%, and NPV 69% for detecting CMR‑confirmed MVO; the figure depicts ~76% accuracy. Top predictive features (highest SHAP values) included high residual active coronary occlusion score and low/absent reperfusion score on post‑PCI ECG, greater pre‑PCI ST‑elevation, small change in occlusion score pre‑ to post‑PCI, and reduced post‑PCI LVEF. The authors note that the absence of these AI features does not exclude MVO.
Conclusion
An AI‑enhanced, pre/post‑PCI ECG strategy showed promising performance for identifying MVO after anterior STEMI, with deliberately high specificity to pinpoint patients most likely to benefit from intensified therapy or monitoring when CMR is unavailable. Findings are internally validated only and require prospective confirmation across broader infarct territories.