Overview
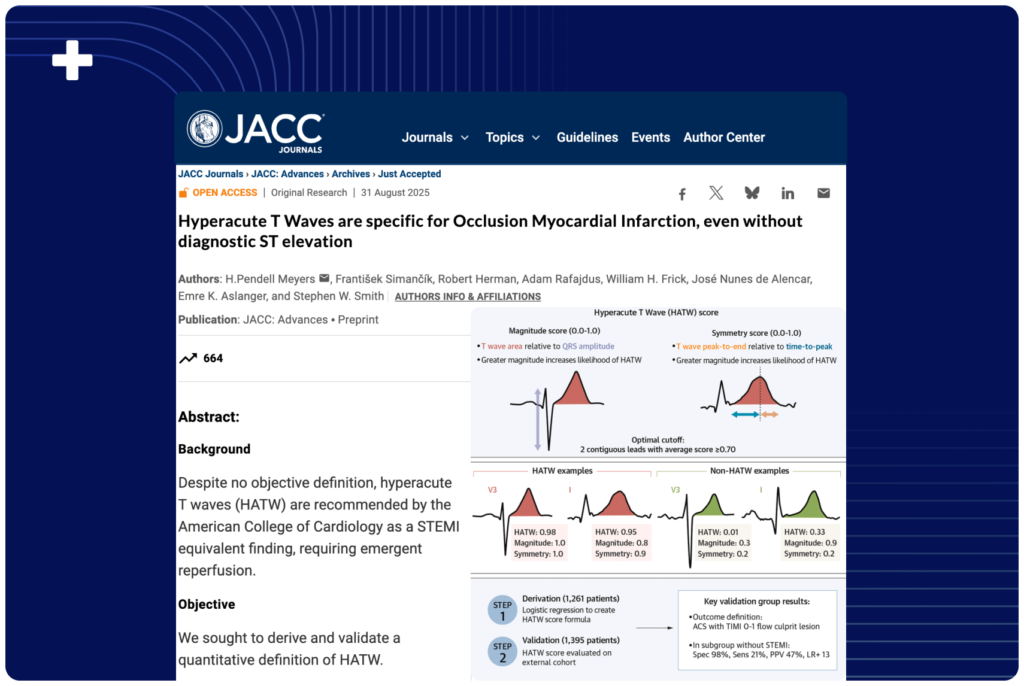
This study aimed to derive and validate a quantitative definition of hyperacute T waves (HATW) by developing the HATW score and evaluating its diagnostic accuracy for identifying acute coronary occlusion in patients with possible ACS but without STEMI criteria.
Published in: The Journal of the American College of Cardiology
Published on: 31 August 2025
Background
Despite no objective definition, hyperacute T waves (HATW) are recommended by the American College of Cardiology as a STEMI equivalent finding, requiring emergent reperfusion.
Methods
We retrospectively evaluated adults with possible ACS across five PCI centers. Exclusions were: lack of pre-angiogram ECG, QRS duration ≥110 ms, and elevated troponin without angiogram. The outcome definition was: myocardial infarction with TIMI 0-1 flow culprit lesion. ECG measures included T wave magnitude (T wave area relative to QRS amplitude) and symmetry (T wave peak-to-end time relative to onset-to-peak time). The HATW score was derived and evaluated on separate groups. The primary analysis was HATW score performance for acute coronary occlusion in patients without STEMI criteria.
Results
3,274 patients were reviewed, and 618 were excluded. 1,261 and 1,395 patients were allocated to derivation and validation groups. In derivation the optimal HATW score threshold for ≥ 98% specificity was: 2 consecutive leads with mean HATW score ≥ 0.7. In validation the performance for acute coronary occlusion in the subset without STEMI criteria (N = 1300) was: 98.4% specificity, 20.7% sensitivity, 47.4% PPV, 12.54 LR+. Among patients without STEMI criteria but positive HATW score, 84% had a culprit lesion causing AMI.
Conclusion
The HATW score is the first objective definition of hyperacute T waves showing significant clinical utility as an ECG finding of acute coronary occlusion in potential ACS patients.