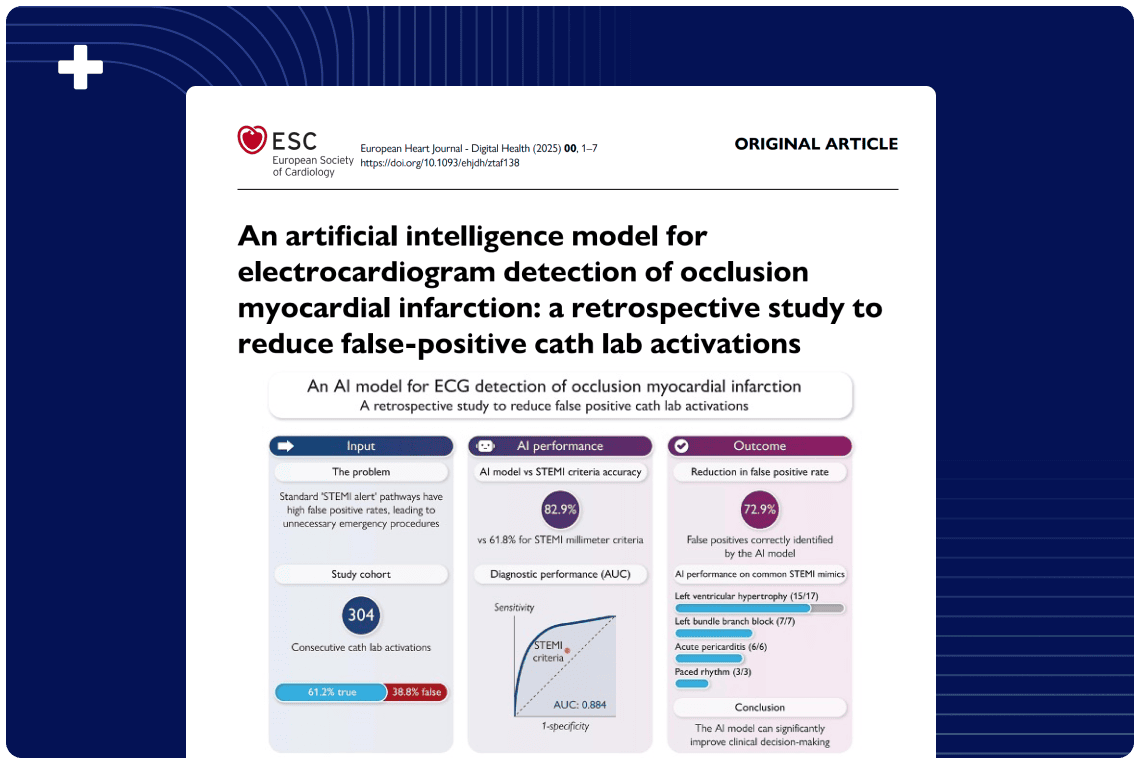
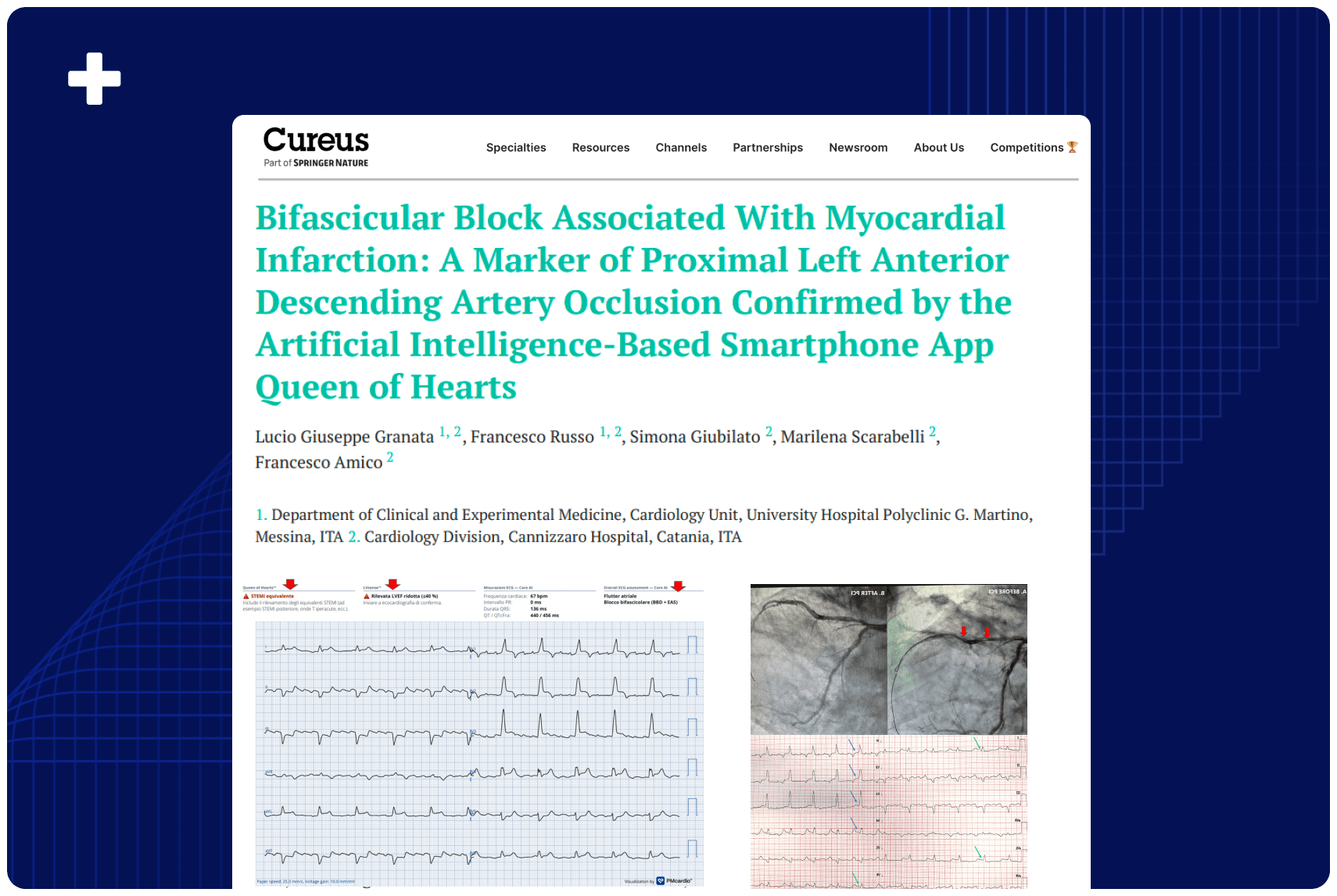
Overview
Across 24 513 consecutive chest-pain presentations to five Swedish emergency departments, the Queen of Hearts (QoH) AI-ECG model detected acute coronary occlusion myocardial infarction with 52 % sensitivity and 99 % specificity. It outperformed an extended STEMI algorithm applied to the same cohort (41 % sensitivity, 95 % specificity) and more than doubled the sensitivity of classic STEMI criteria (55 % versus 26 %) while preserving comparable specificity (99 % versus 98 %). This real-world validation demonstrates that QoH markedly improves early ECG recognition of OMI in unselected, non-traumatic chest-pain patients.
Presented at: Swedish Cardiovascular Spring Meeting, Malmö
Event Date: 9 – 11 April 2025
Background
The Queen of Hearts (QoH) ECG artificial intelligence (AI) model (PMcardio, Bratislava, Slovakia) has demonstrated improved sensitivity for detecting occlusion myocardial infarction (OMI) compared with STEMI criteria, but further validation in all-comer cohorts is needed. We aimed to evaluate QoH’s diagnostic performance for OMI detection in chest pain patients at Swedish emergency departments (EDs) and compare its accuracy to STEMI criteria.
Methods
This retrospective analysis utilized data from the ESC-TROP study, identifying all consecutive chest pain patients presenting at five southern Sweden EDs in 2017–2018. Patients with suspected STEMI who transferred directly to the coronary care unit, i.e. bypassing the ED were not included. OMI was defined as acute myocardial infarction due to coronary occlusion based on angiographic and adjudication data.
QoH was applied to all cases, while STEMI criteria were applied only to patients without left bundle branch block (LBBB), ventricular pacing, or left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH). Previously established diagnostic algorithms for OMI detection in specific situations, e.g. LBBB/ventricular pacing and LVH, were integrated with an extension of conventional STEMI criteria (e.g., ST elevation in additional contiguous leads: -III/aVL, II/-aVR, -aVR/I, III/-aVL, -V1/-V2, and -V2/-V3) into an extended algorithmic diagnostic approach which was evaluated in all patients.
Results
Among 24,513 chest pain patients (mean age 59±19 years, 52% male), 467 (1.9%) had OMI. QoH yielded 52% sensitivity, 99% specificity, 51% positive predictive value (PPV), and 99% negative predictive value (NPV) when applied to all patients.
The extended algorithmic approach yielded 41% sensitivity, 95% specificity, 13% PPV, and 99% NPV. In the subgroup of patients where STEMI criteria were applicable, QoH showed higher sensitivity (55%) and PPV (52%) than STEMI criteria (26% and 17%, respectively) with similar specificity (QoH: 99%; STEMI criteria: 98%) and NPV (QoH: 99%; STEMI criteria: 99%).
Conclusion
In unselected ED patients with non-traumatic chest pain, QoH significantly improved ECG detection of OMI compared to currently available ECG criteria.

Authors: Thomas Lindow¹ ², Axel Nyström³ ⁴, Arash Mokhtari¹ ⁵, Robert Herman⁶ ⁷, H Pendell Meyers⁸, Stephen W Smith⁹, Jakob Lundager Forberg¹ ¹⁰, Ulf Ekelund¹ ⁵